Creating Datasets
Why Would You Create Datasets?
The dataset entity is one the most important entities in the metadata model. They represent collections of data that are typically represented as Tables or Views in a database (e.g. BigQuery, Snowflake, Redshift etc.), Streams in a stream-processing environment (Kafka, Pulsar etc.), bundles of data found as Files or Folders in data lake systems (S3, ADLS, etc.). For more information about datasets, refer to Dataset.
Goal Of This Guide
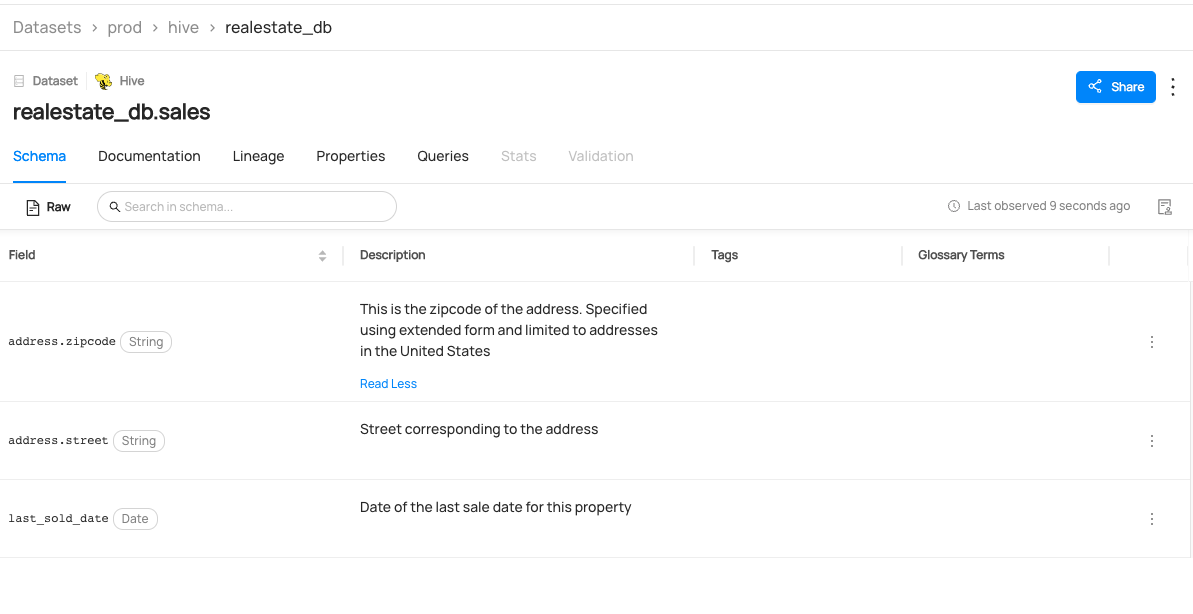
This guide will show you how to create a dataset named realestate_db.sales with three columns.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you need to deploy DataHub Quickstart and ingest sample data. For detailed steps, please refer to Datahub Quickstart Guide.
Create Datasets With GraphQL (Not Supported)
🚫 Creating a dataset via
graphqlis currently not supported. Please check out API feature comparison table for more information,
Create Datasets With Python SDK
The following code creates a Hive dataset named realestate_db.sales with three fields and a URN of urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,realestate_db.sales,PROD):
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/dataset_schema.py
# Imports for urn construction utility methods
from datahub.emitter.mce_builder import make_data_platform_urn, make_dataset_urn
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Imports for metadata model classes
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import (
AuditStampClass,
DateTypeClass,
OtherSchemaClass,
SchemaFieldClass,
SchemaFieldDataTypeClass,
SchemaMetadataClass,
StringTypeClass,
)
event: MetadataChangeProposalWrapper = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=make_dataset_urn(platform="hive", name="realestate_db.sales", env="PROD"),
aspect=SchemaMetadataClass(
schemaName="customer", # not used
platform=make_data_platform_urn("hive"), # important <- platform must be an urn
version=0, # when the source system has a notion of versioning of schemas, insert this in, otherwise leave as 0
hash="", # when the source system has a notion of unique schemas identified via hash, include a hash, else leave it as empty string
platformSchema=OtherSchemaClass(rawSchema="__insert raw schema here__"),
lastModified=AuditStampClass(
time=1640692800000, actor="urn:li:corpuser:ingestion"
),
fields=[
SchemaFieldClass(
fieldPath="address.zipcode",
type=SchemaFieldDataTypeClass(type=StringTypeClass()),
nativeDataType="VARCHAR(50)", # use this to provide the type of the field in the source system's vernacular
description="This is the zipcode of the address. Specified using extended form and limited to addresses in the United States",
lastModified=AuditStampClass(
time=1640692800000, actor="urn:li:corpuser:ingestion"
),
),
SchemaFieldClass(
fieldPath="address.street",
type=SchemaFieldDataTypeClass(type=StringTypeClass()),
nativeDataType="VARCHAR(100)",
description="Street corresponding to the address",
lastModified=AuditStampClass(
time=1640692800000, actor="urn:li:corpuser:ingestion"
),
),
SchemaFieldClass(
fieldPath="last_sold_date",
type=SchemaFieldDataTypeClass(type=DateTypeClass()),
nativeDataType="Date",
description="Date of the last sale date for this property",
created=AuditStampClass(
time=1640692800000, actor="urn:li:corpuser:ingestion"
),
lastModified=AuditStampClass(
time=1640692800000, actor="urn:li:corpuser:ingestion"
),
),
],
),
)
# Create rest emitter
rest_emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server="http://localhost:8080")
rest_emitter.emit(event)
Note that the name property of make_dataset_urn sets the display name of the dataset.
After creating the dataset, you can perform various manipulations, such as adding lineage and custom properties. Here are some steps to start with, but for more detailed guidance, please refer to the What's Next section.
Add Lineage
The following code creates a lineage from fct_users_deleted to realestate_db.sales:
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Construct a lineage object.
lineage_mce = builder.make_lineage_mce(
[
builder.make_dataset_urn("hive", "fct_users_deleted"), # Upstream
],
builder.make_dataset_urn("hive", "realestate_db.sales"), # Downstream
)
# Create an emitter to the GMS REST API.
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter("http://localhost:8080")
# Emit metadata!
emitter.emit_mce(lineage_mce)
For more information on adding lineages, please refer to how to add lineage on a dataset using PythonSDK.
Add custom properties
You can also set custom properties using the following code:
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/dataset_add_properties.py
import logging
from typing import Union
from datahub.configuration.kafka import KafkaProducerConnectionConfig
from datahub.emitter.kafka_emitter import DatahubKafkaEmitter, KafkaEmitterConfig
from datahub.emitter.mce_builder import make_dataset_urn
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DataHubRestEmitter
from datahub.specific.dataset import DatasetPatchBuilder
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# Get an emitter, either REST or Kafka, this example shows you both
def get_emitter() -> Union[DataHubRestEmitter, DatahubKafkaEmitter]:
USE_REST_EMITTER = True
if USE_REST_EMITTER:
gms_endpoint = "http://localhost:8080"
return DataHubRestEmitter(gms_server=gms_endpoint)
else:
kafka_server = "localhost:9092"
schema_registry_url = "http://localhost:8081"
return DatahubKafkaEmitter(
config=KafkaEmitterConfig(
connection=KafkaProducerConnectionConfig(
bootstrap=kafka_server, schema_registry_url=schema_registry_url
)
)
)
dataset_urn = make_dataset_urn(platform="hive", name="fct_users_created", env="PROD")
with get_emitter() as emitter:
for patch_mcp in (
DatasetPatchBuilder(dataset_urn)
.add_custom_property("cluster_name", "datahubproject.acryl.io")
.add_custom_property("retention_time", "2 years")
.build()
):
emitter.emit(patch_mcp)
log.info(f"Added cluster_name, retention_time properties to dataset {dataset_urn}")
For more information on adding custom properties, please refer to Modifying Custom Properties on Datasets
We're using the MetdataChangeProposalWrapper to change entities in this example.
For more information about the MetadataChangeProposal, please refer to MetadataChangeProposal & MetadataChangeLog Events.
Expected Outcomes
You can now see realestate_db.sales dataset has been created.
What's Next?
Now that you created a dataset, how about enriching it? Here are some guides that you can check out.
